164
ANNUAL ACCOUNTS /
Notes to the consolidated accounts
Valuation methods used
Based on a multi-criteria approach, the valuation methods used by
the real estate experts are the following:
Discounted estimated rental value method
This method involves capitalising the property’s estimated rental
value by using a capitalisation rate (yield) in line with the real estate
market. The choice of the capitalisation rate used depends essen-
tially on the capitalisation rates applied in the property investment
market, taking into consideration the location and the quality of
the property and of the tenant at the valuation date. The rate cor-
responds to the rate anticipated by potential investors at the valua-
tion date. The determination of the estimated rental value takes into
account market data, the property’s location, it’s quality, the number
of beds for healthcare assets and, if available, the tenant’s financial
data (EBITDAR).
The resulting value must be adjusted if the current rent generates an
operating income above or below the estimated rental value used for
the capitalisation. The valuation also takes into account the costs to
be incurred in the near future.
Discounted cash flow method
This method requires an assessment of the net rental income gen-
erated by the property on an annual basis during a defined period.
This flow is then discounted. The projection period generally varies
between 10 and 18 years. At the end of this period, a residual value is
calculated using the capitalisation rate on the terminal value, which
takes into account the building’s expected condition at the end of
the projection period, discounted.
Market comparables method
This method is based on the principle that a potential buyer will not
pay more for the acquisition of a property than the price recently
paid on the market for the acquisition of a similar property.
Residual value method
The value of a project is determined by defining what can/will be
developed on the site. This means that the purpose of the project
is known or foreseeable in terms of quality (planning) and quantity
(number of square meters that can be developed, future rents, etc.).
The value is obtained by deducting the costs to completion of the
project from its anticipated value.
Other considerations
If the fair value cannot be determined reliably, the properties are val-
ued at the historical cost. In 2014, the fair value of all properties could
be determined reliably so that no building was valued at historical
cost.
In the event that the future selling price of a property is known at the
valuation date, the properties are valued at the selling price.
For the buildings for which several valuation methods were used, the
fair value is the average of the results of these methods.
During the year 2014, there was no transfer between valuation levels
(within the meaning of IFRS 13) 1, 2 and 3. In addition, there was no
change in valuation methods for the investment properties.
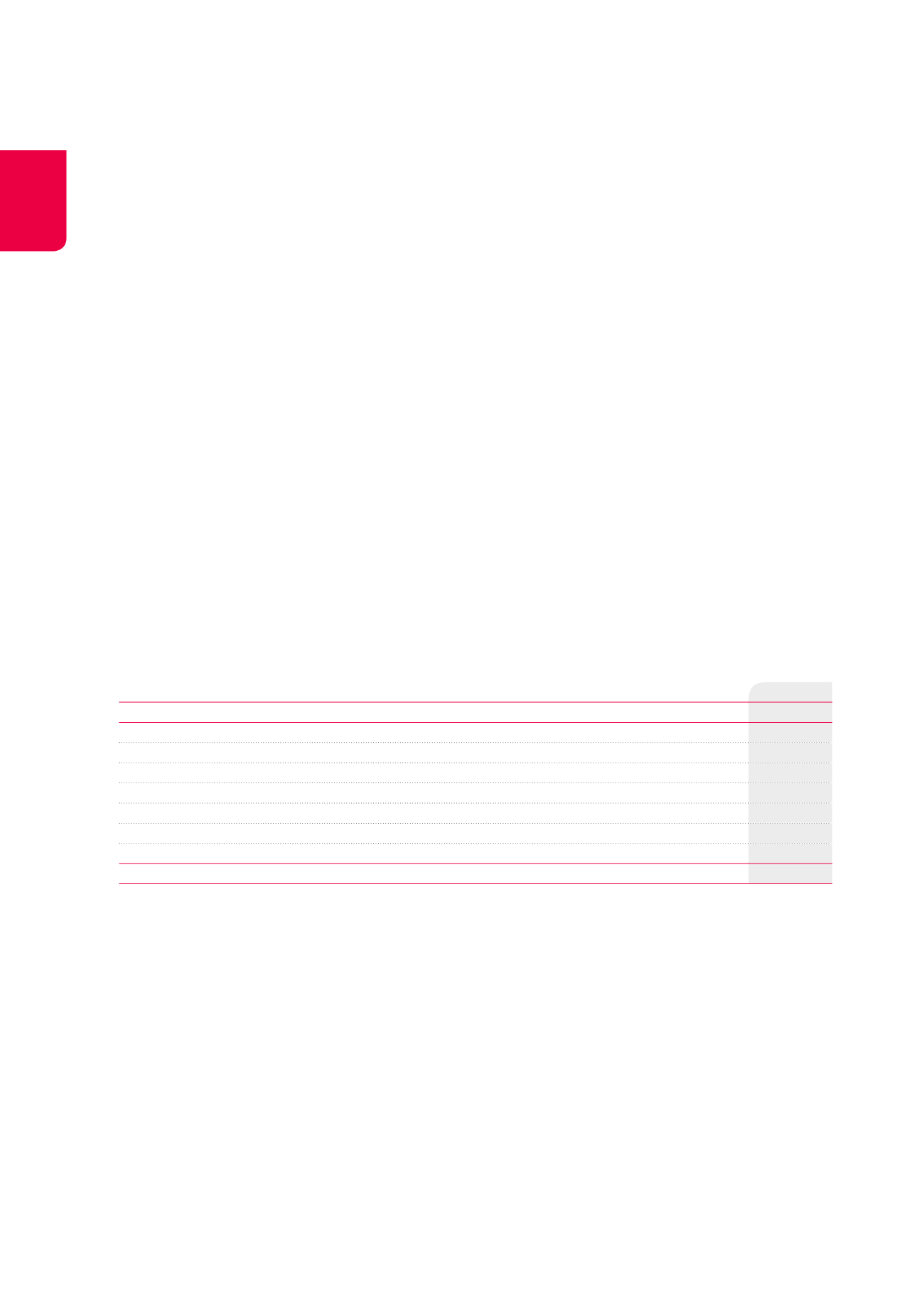
Changes in the fair value of investment properties, based on unobservable data
(x €1,000)
FAIR VALUE AT 31.12.2013
3,347,009
Gains/losses recognised under the income statement
-5,456
Acquisitions
71,398
Extensions/redevelopments
24,417
Investments
38,854
Writeback of lease payments sold
15,931
Disposals
-292,970
Transfers of levels
FAIR VALUE AT 31.12.2014
3,199,183